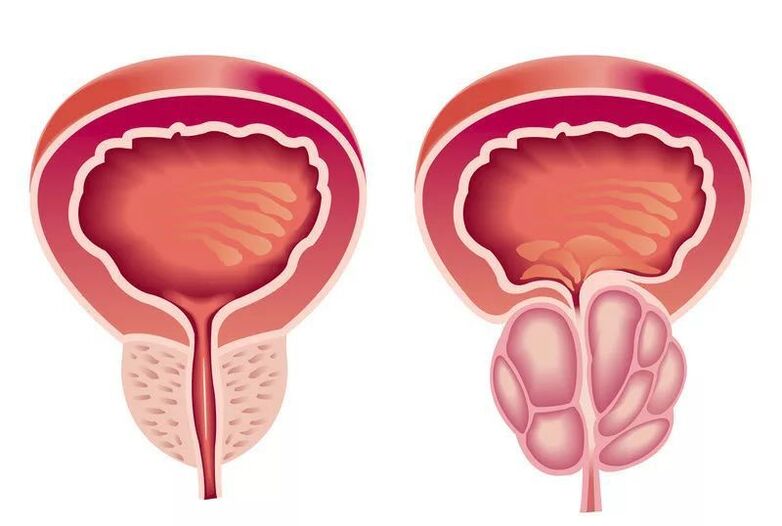
Inflammation of the prostate today is the leader in the group of male diseases, which are transmitted mainly through sexual contact. Its complications threaten infertility, decreased libido, impotence.
The first symptoms of prostatitis in men
Prostatitis is an inflammatory disease. This is one of the most common urological pathologies, which is diagnosed in representatives of the strong half of humanity.
This anomaly is most often found in men older than thirty, although the disease has recently become much younger. Treatment of prostatitis should be carried out by qualified specialists (urologists or andrologists), because there is a high probability of developing various complications.
How is prostatitis treated?
With the help of drugs
- NSAIDs - relieve inflammation, fever and chills. They have a mild analgesic effect. With the onset of prostatitis, short-term treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs and taking vitamins is needed to keep the gland in a normal state. Men are prescribed: Diclofenac, Nise, Voltaren, Nimesulide. Medicines are produced in suppositories, tablets, injections.
- Antibiotics - designed to remove the infectious or bacteriological factor of inflammation. The prostatitis treatment regimen is signed after the pathogen has been identified and its antibiotic resistance tested. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. In severe cases, the therapy is extended to two weeks.
- Hormones are recommended if the usual course of medication has not been helpful, as well as in reducing sexual desire due to advanced disease. Treatment with hormones at an early stage is prohibited. Medications are taken under the strict supervision of a urologist.
- Symptomatic medications - take Aspirin tablets to eliminate the pain syndrome. No-shpa removes cramps. Novocaine blockade is indicated for persistent intense pain.
- Vitamins and medications to maintain prostate function in good condition. During the period of remission, it is recommended to take medications to normalize metabolism and improve the blood supply to glandular tissue and juice production. For that, phytopreparations are prescribed: Prostamol-Uno, Prostate-forte and the like. To strengthen the immune system, a complex of vitamins and minerals has been shown: Duovit, Vitrum.
Self-medication is dangerous, it does more harm than good. It is necessary to consult a urologist before taking any of these medications.
With the use of physiotherapy
- UHF and microwave.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Cure with mud.
- Galvanization.
- Ultraphonophoresis.
- Laser treatment.
- Heat therapy.
natural remedies
Diagnosis
In order to start the treatment of prostatitis in time, it is necessary to contact a competent specialist who will conduct a comprehensive examination and make a correct diagnosis. The list of recommended diagnostic methods includes the following:
- Blood tests - do a study of the biochemical composition, for the content of PSA (prostate-specific antigen), general analysis and PCR if necessary.
- Urine analysis - a man is asked to urinate in several different containers in order to conduct the study in different ways.
- Scraping from the surface of the urethral canal to detect an infectious pathogen.
- Bacteriological culture of prostate and urethral secretions for determination of bacterial pathogen and its drug resistance.
- Prostate ultrasound - allows you to assess the size and shape of the gland, the presence or absence of tissue fusion, adhesions and cicatricial changes.
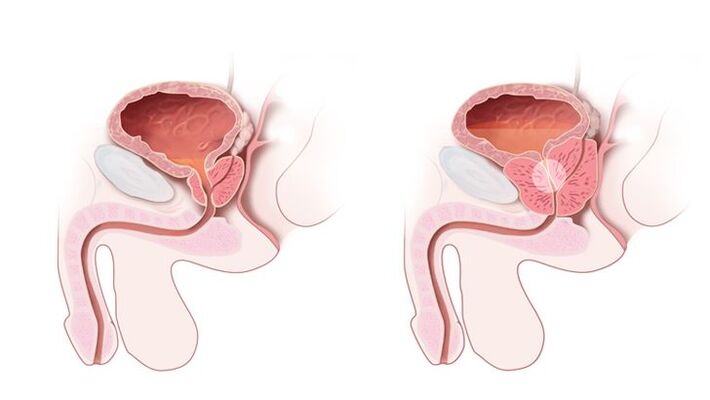
An obligatory item in the diagnosis of prostatitis is a rectal digital examination. Examination of the fingers allows the doctor to feel the gland and assess its density, structure, shape and size. Also, during the rectal examination, the secret of the prostate was obtained, which is then sent for analysis. Additional examination methods are assigned to the individual patient individually, if indicated.
These can be urine flow rate measurements, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography, pelvic X-rays and other methods.
Acute prostatitis
The disease begins with a sudden rise in temperature (up to 40 degrees), a terrible headache, fever. Symptoms that occur are accompanied by pain in the groin, perineum, back, urethral discharge, frequent urination, and a constant urge to urinate.
Bladder emptying occurs with a delay, a burning sensation. The urine itself becomes cloudy, and blood may appear in it. There is irritability, fatigue.
The outcome of acute prostatitis can be a complete resolution of the process (with timely treatment). Since the changes occur in many organs of the small pelvis, they cannot be left to chance because otherwise corresponding complications will arise:
- Vesiculitis is an inflammation of the seminal vesicles, the cause of the formation of pus in the semen, which not only reduces the quality of the ejaculate, but also leads to a loss of reproductive function.
- Coliculitis - inflammatory changes of the seminal tubercle become the reason for the development of severe pain during sex, interruption of orgasm, impotence of a psychological nature.
- The formation of an abscess in the body of the prostate, its rupture, purulent damage to the rectum leads to worsening of symptoms, severe intoxication of the body, to death.
- Stagnation in the tissues of the prostate leads to changes in their structure, disruption of innervation, blood supply, both the glands themselves and nearby organs, in violation of their functions. Erection becomes insufficient for full sexual intercourse, premature ejaculation is observed, prolonged sexual intercourse without orgasm.
- Cicatricial changes in the gland, the seminal vesicle lead to infertility, a decrease in the qualitative composition of sperm and sperm motility. Narrowing of the urethra interferes with the normal process of urination, bladder obstruction can cause acute urinary retention, which requires urgent surgical assistance.
The main symptoms
As noted above, the disease can be chronic and acute. Frequent and one of the most important symptoms is increased urination. A healthy man usually does not experience more than 10-11 urges to urinate during the day (the normal number is 5-6 urges).
As a result of the development of inflammation of the prostate, there is a negative effect on the bladder, so in the presence of the disease the following symptoms will appear:
- Increase in the number of urges (while the daily amount of urine remains the same).
- Urine is excreted in small portions, which is associated with the reception of false signals from the receptors of the urinary bladder due to the presence of an inflammatory process. Also, therefore, there may be a feeling that the bladder is full even after emptying.
- Pain during urination, which occurs due to narrowing of the urethra due to the inflammatory process in the prostate.
- Difficulty urinating due to compression of certain areas of the urethra by inflammation. In some cases, men are therefore unable to empty their bladder at all.
- At night, the walls of the bladder begin to give false signals, which increases the number of trips to the toilet during sleep.

Part of the diagnosis of prostatitis can also be made by monitoring body temperature, along with problems related to urination. If these problems are accompanied by an increase in temperature to subfebrile and febrile values, then with a high degree of probability we can talk about the development of pathology. It is important to note that in the later stages of the disease, on the contrary, a decrease in body temperature to 35, 5-36 degrees can be noticed, which is in any case an extremely negative and dangerous symptom, which should not be allowed.
In the middle stages of the disease, blood can be seen in the patient's urine. This sign is relatively rare and often not indicative, but extremely dangerous. It can begin to manifest due to purulent prostate fusion, prostate trauma, as well as in cases of complications of the inflammatory process with hyperplasia. Treatment in this case is complicated (surgery is often necessary).
Treatment should be started immediately after the onset of the first symptoms of the disease. If there have been at least some, albeit seemingly insignificant, urination problems, which in some cases are accompanied by fever and pain in the area of ease, an examination by a urologist should be scheduled immediately to clarify the diagnosis. It is necessary to pay attention to the signs of pathology described above, because only with timely treatment, it is possible to beat prostatitis quickly and painlessly.
Why does the prostate become inflamed?
In fact, there are only 2 main reasons:
- Infection. Most often, prostatitis develops precisely because of a prostate infection. Infection can occur through the bladder, urethra, rectum, blood and lymph. It turned out that prostatitis itself is often a complication of an existing disease. Therefore, never self-medicate, you must first cure the source of the infection. Cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, STIs (sexually transmitted infections) - this is understandable, they are directly related to the prostate. Even untreated tonsillitis, sinusitis, flu, tooth decay can come back and haunt prostate inflammation.
- Circulatory disorders. This can be due to structural characteristics, and due to spasms of the urethra, disorders of nerve conduction and work of the muscles of the abdomen and pelvis, as well as due to external factors.
However, whether prostatitis develops or not depends primarily on predisposing factors:
- Chaotic sex life. Plenty of sexual partners, especially unprotected contacts - this depletes the immune system, which must constantly deal with foreign microflora in female secretions. And sooner or later it fails.
- Long abstinence. This is the other extreme. Lack of sex has a bad effect on the general condition of men, and especially on the prostate. His secretion stagnates, blood circulation is disturbed, an infection develops.
- Masturbation. It happens that men try to escape the lack of sex by masturbating. However, it causes a decrease in prostate tone, it becomes lethargic. It is even isolated in a special type of prostatitis - congestive.
- Excess weight. In overweight men, the load on the pelvic organs, as well as the whole body in general, is significantly increased. The blood supply is disturbed, which leads to prostatitis, hemorrhoids and other diseases.
- Hypothermia. "Don't sit in the cold, " they tell all the girls. However, this also applies to men. Fans of extreme winter fun, passionate fishermen, owners of old cars are in danger (yeah, how I often see men lying on the cardboard under the car in winter). even passengers on frozen trains, as well as fashion lovers of wrapped pants and no. Hat. Oh yes, and urinating outside in winter is also fraught with serious consequences.
- Inactivity. Basically, this refers to the workflow, when you have to sit in one place for a long time: drivers, office workers. It is especially harmful to cross your legs, because the load on the prostate only increases.
- Stress. Psychological problems, chronic lack of sleep, overloaded work schedule are favorite infections.
- Restraining the urge to urinate. Are the 5 minutes saved in a hectic workflow worth the potential problems?
- Bad habits. So, where without them? Alcohol and nicotine abuse that only violates.
- Wrong diet. Fatty, spicy, salty foods are a magnet for diseases of the pelvic organs.
- background diseases. Any untreated infectious disease can be complicated by prostatitis.
- Tight underwear. As well as "fashionable" too tight pants. They constrict the small pelvis, disrupt blood circulation, cause swelling and inflammation.
- Physical overload. Professional athletes, loaders, active gym visitors are at great risk.
- Self-medication. Sometimes men are ashamed to admit their problems even to a doctor, they try to break the disease with various folk remedies, tested and not so good. However, it happens that without medication prescribed by a competent doctor, it cannot be worn here.

How is the disease diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made by a urologist or andrologistafter examining the patient, collecting a medical history, and studying the symptoms. The doctor should determine the method of contraception of the patient, the presence of sexually transmitted infections in the sexual partner, the possibility of anal intercourse without a condom. This data facilitates diagnosis and directs the physician’s thinking in the right direction. Prescribing the appearance of symptoms of disease or discomfort in the perineum allows us to assess the course of prostatitis and its severity. The urologist necessarily examines the patient's genitals and performs a rectal examination of the prostate. To do this, he inserts one finger into the patient's anus and touches the front wall of the rectum, which protrudes from the prostate. Pain and its size indicate the intensity of the inflammatory process.
Then, the doctor conducts a series of instrumental, microscopic, bacteriological, and immunological studies to clarify the cause of the disease. The most common diagnostic method is a 4 or 3 cup urine sample. The first method is more time consuming and more difficult to implement in practice, as it requires the patient to intentionally stop urinating several times. The second modification is simpler: the patient urinates continuously in three different containers in equal portions. The first part talks about the condition of the urinary tract, the second about the pathology of the urinary bladder and kidneys, and the third part provides information about the condition of the prostate. All collected material is examined under a microscope. In prostatitis, white blood cells and sometimes bacteria are found in the third part of the urine.
The secretion of the prostate is also taken for microscopy.To do this, the doctor massages the prostate through the wall of the rectum for a while so that it empties into the urethra. Swabs are made from the material collected in the laboratory, stained and studied under high magnification. The sign of inflammation is leukocytes, the bacterial etiology of the disease is bacteria in the swab. To determine the type of pathogen, the secretion of the prostate is inoculated on nutrient media. If pathogenic microorganisms are present in it, then after 3-5 days they form colonies of microbes which can then be studied. The bacteriological method enables obtaining data on the sensitivity of the microflora to antibiotics.
Of the instrumental diagnostic methods, the following are performed:
- Kidney ultrasound;
- TRUS of the prostate with dopplerography - an ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum for the best visualization of the prostate, its blood flow is additionally assessed;
- Ascending uroretrography is necessary for persistent recurrent prostatitis. The radiopaque substance is injected into the urethra, after which a series of successive images are taken.
In addition to these methods, all types of research on sexually transmitted diseases are of great importance. Among them are:
- PCR ejaculate, prostate secretion, scraping of the urethral mucosa - the method allows you to detect a wide range of pathogens;
- Blood ELISA - to detect specific antibodies to STI pathogens.
Types of prostatitis
According to the 1995 criteria of the American National Institutes of Health (NIH USA), there are four categories of prostatitis:
- Category I: Acute prostatitis;
- Category II: Chronic bacterial prostatitis;
- Category III: Chronic prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP / CPPS);
- Category IIIa: Chronic prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome with signs of inflammation;
- Category IIIb: Chronic prostatitis / chronic pelvic pain syndrome without signs of inflammation;
- Category IV: Asymptomatic (asymptomatic) chronic prostatitis.
Occasionally, chronic granulomatous prostatitis occurs, which is not mentioned in this classification.
In turn, most experts distinguish:
According to the course of the disease:
- acute prostatitis;
- chronic prostatitis;
Depending on the cause of the disease:
- bacterial prostatitis;
- nonbacterial prostatitis
In most cases (especially in men under the age of 40), bacterial prostatitis is noted.
Based on this there are:
- acute bacterial prostatitis;
- chronic bacterial prostatitis;
- chronic abacterial prostatitis.
Prevention
To prevent the onset of inflammation or recurrence of chronic pathology, you must follow these recommendations:
- Reduce the amount of alcohol consumed;
- Do sports regularly;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Quit smoking;
- Avoid stressful situations;
- Treat inflammation on time - first of all, it refers to genital infections;
- Take a contrast shower;
- Avoid lifting heavy objects;
- Use barrier methods of contraception;
- Have sex regularly;
- Take vitamin preparations;
- Get involved in boosting immunity;
- Visit a urologist twice a year;
- Eat properly and balanced.
The purpose of the prostate in the male body: what is it responsible for?
The prostate is an exocrine gland in the male body.
Iron belongs to the reproductive system and is responsible for the production of a number of specific substances:
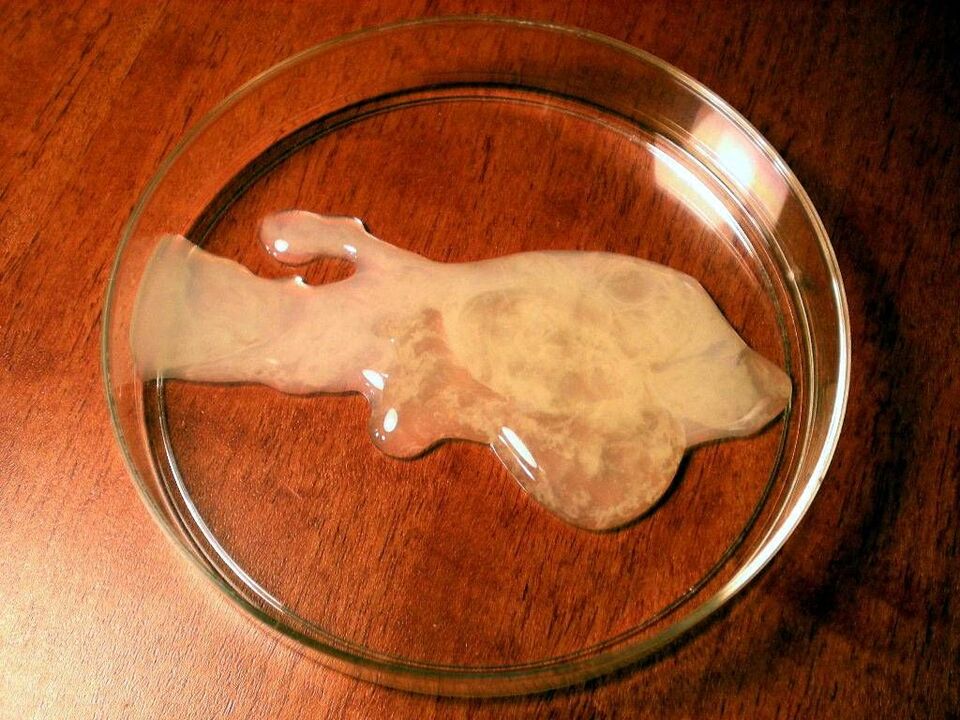

- the main secret is (prostate juice), which ensures the required viscosity of the ejaculate and, consequently, the normal motility of the sperm. When sperm is too thick, fertilization is difficult, and a woman simply cannot get pregnant from a seemingly healthy man;
- other components maintain normal sperm composition. This includes biologically active substances, immunoglobulins, enzymes, vitamins, microelements, etc. The norms of these substances are individual, and it is the prostate that regulates their content.
Thus, she is responsible for a man's reproductive abilities, for the possibility of a regular and full sexual life and the birth of children. This is the main function of the gland, but there are others, no less important.